Describe the Role of Dna Helicases During Replication
They unwind the DNA with the help of ATP hydrolysis and thus facilitate the replication and transcription processes. The 3 --- 5 exonuclease activity of DNA polymerase.
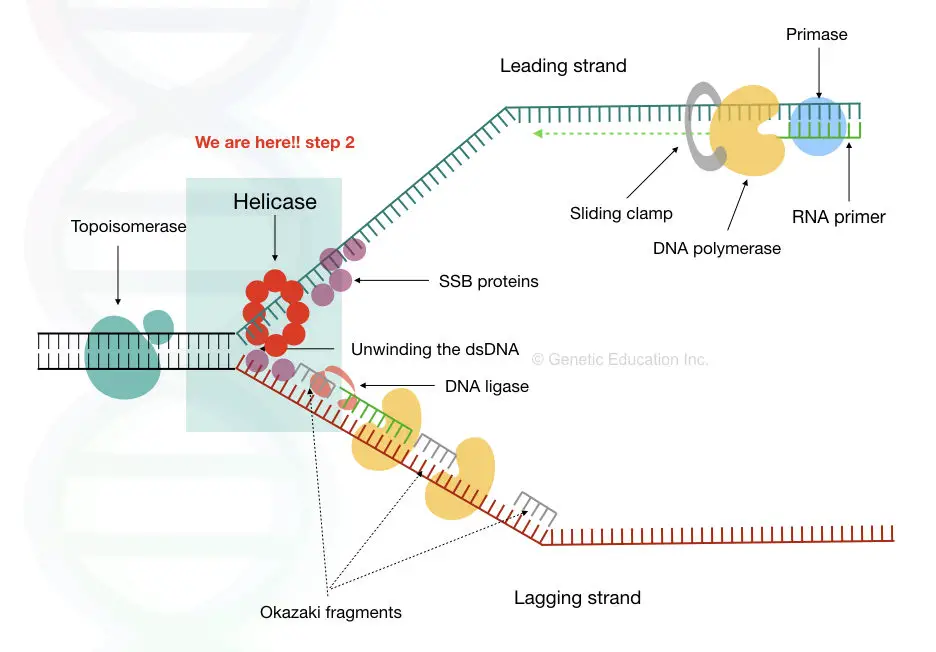
What Is Helicase And How It Unwinds Dna Genetic Education
DNA polymerases add complementary nucleotides Describe the role of helicases and DNA polymerases during DNA replication.

. DNA polymerase performs several functions during replication. The activity of DNA helicase at the replication fork generates torsional strain upstream to the replication fork. Unwinds double-stranded DNA during replication In addition.
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae homolog of WRNIP1 Mgs1 maintenance of genome stability 1 is an. The human RecQ helicases and their orthologs in other organisms all fulfill important roles in DNA replication and repair. Here we describe the roles of ChlR1 in DNA replication recovery.
DNA helicases catalyze the break up of the hydrogen bonds between strands. DNA replication copies the DNA and its genes each time a cell divides so newly formed cells have the correct gene material. DNA helicases are essential during DNA replication because they separate double-stranded DNA into single strands allowing each strand to be copied.
Each of the new DNA molecules has conserved one of the two original DNA strands. DNA helicase disrupts the hydrogen bonding between base pairs to separate the strands into a Y shape known as the replication fork. Coli of DNA helicase which.
The homology of WRNIP1 to members of the replication factor C family and its ability to stimulate the DNA-synthesis activity of DNA polymerase δ 3 suggest a possible role for WRNIP1 in DNA replication andor replication-related DNA transactions. The main function of DNA polymerase is to synthesize a new DNA strand. It runs ahead of the replication fork and continuously unwinds the dsDNA providing the template for DNA polymerase to work.
Helicases in DNA Replication The first step of DNA replication is to unwind the double stranded structure in order to promote semi-conservative replication. Describe why DNA replication is considered semi-conservative One original and one new strand composes the DNA making it semi-conservative. This area will be the template for replication to begin.
Helicases are enzymes that bind and may even remodel nucleic acid or nucleic acid protein complexes. Binding of DNA around an initiator protein complex DNA-A ATP 30-40. Learn the definition of.
In each new DNA double helix one. DNA polymerases textbf DNA polymerases DNA polymerases. 2 rows DNA helicase is an enzyme that unwinds DNA to allow for replication.
Briefly describe the biochemical role of the following enzymes in DNA replication. Comprehensive recent reviews of the RecQ helicases and their biological functions are available Chu and Hickson 2009. Unless DNA helicase unwinds dsDNA DNA polymerase can not able to add nucleotide.
DNA helicases are enzymes that are able to unwind DNA by the use of the energy-equivalent ATP. There are DNA and RNA helicases. DNA helicase is an ATP dependent catalytic enzyme which unwinds the dsDNA for providing leading as well as lagging strand replication.
Three basic steps involved in DNA replication are Initiation elongation and termination. DNA is directional in both strands signified by a 5 and 3 end. They play essential roles in DNA replication DNA repair and DNA recombination in all organisms.
However the mechanism by which ChlR1 preserves genomic integrity is largely unknown. Type I topoisomerases relax DNA ie remove supercoils by nicking and closing one strand of duplex DNA see Figure 1214. The DNA B or helicase unwinds ori C origin of replication and extends the single stranded region for copying.
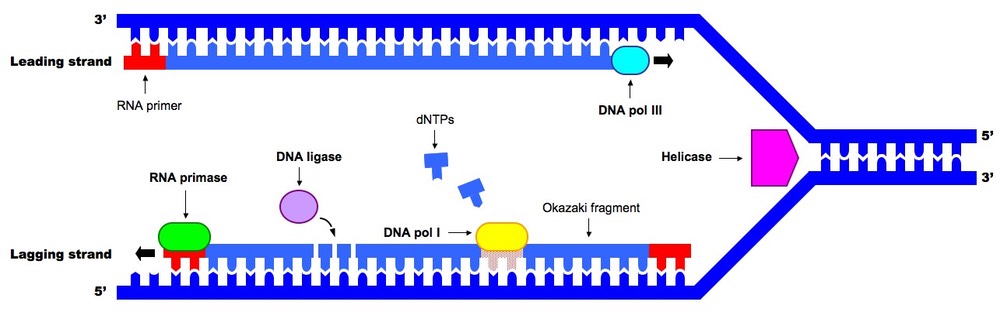
DNA helicases catalyze the break up of the hydrogen bonds between strands. Primase synthesizes RNA primers. This process is mediated by an enzyme.
Separate strands of DNA textbf separate strands of DNA separate strands of DNA. Proofreading helps to maintain the integrity of the double-stranded DNA. DNA helicase unwinds dsDNA at the replication fork to generate ssDNA strands.
DNA helicases are also called molecular motors. It requires ATP and can unwind DNA in both 5-3 and 3-5 direction. DNA Helicase unwinds and unzips the DNA double helix.
The ChlR1 DNA helicase is mutated in Warsaw breakage syndrome characterized by developmental anomalies chromosomal breakage and sister chromatid cohesion defects. DNA polymerases add complementary nucleotides state why DNA replication is a semi-conservative process in each new DNA double helix one strand is from the original molecule and one is new. They break the hydrogen bonds that form between the nitrogenous bases thus connect the chains.
Helicase unwinds the DNA. This is performed by an enzyme known as DNA helicase. Checks newly synthesized DNA and will remove mismatched nucleotides.
Helicases which can unwind the DNA duplex thereby inducing formation of supercoils and topoisomerases which catalyze addition or removal of supercoils. Helicases textbf Helicases Helicases. A critical property of the DNA helicases that play a role in counteracting replication stress consists in their ability to untangle alternative DNA structures that can arise at genomic loci containing repetitive sequences such as centromeres telomeres ribosomal rRNA gene clusters and fragile sites.
Apart from this DNA polymerase is also involved in correcting the errors of added nucleotides in a process known as proofreading.

Dna Helicase Overview Role Function Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Helices In Dna Replication Function Model What Do Helices Do In Dna Replication Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Comments
Post a Comment