Cyclical Unemployment Is Best Described as Unemployment Arising From
In a recession cyclical unemployment will tend to rise sharply. Frictional Structural unemployment C.
What Is Cyclical Unemployment Education Is Around
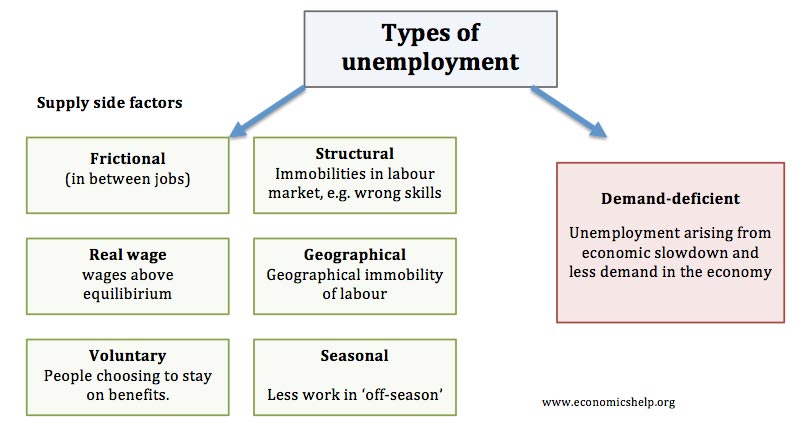
If an economy enters a recession and an employee loses his job and remains unemployed then the economy recovers and his employer rehires him this is best classified as cyclical unemployment Unemployment arising from a persistent mismatch between skills and characteristics of workers and the requirements of jobs is called.
. The Natural Rate of Unemployment The Natural Rate of Unemployment NRU is the sum of. Frictional Structural Cyclical unemployment. A deficiency of spending on goods and services D the everyday dynamics of a free labor market with workers voluntarily changing.
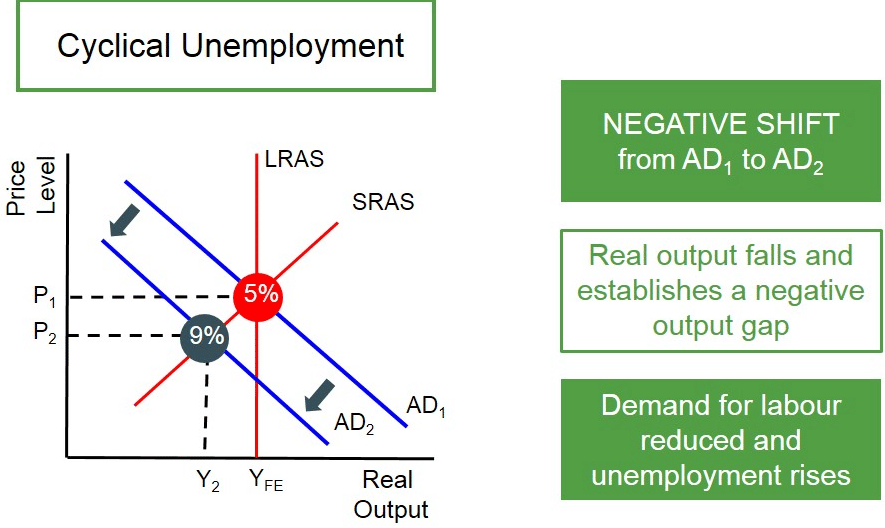
Cyclical unemployment is BEST described as unemployment arising from A the elimination of jobs as a result of technological change. Frictional and structural unemployment. The normal up and down movements in the economy as it cycles through booms and recessions over time.
The decreasing relative importance of goods and the increasing relative importance of services in the US economy B. Frictional Cyclical unemployment d. Wrong - cyclical unemployment D A worker undergoes on-the-job training.
Wrong structural unemployment B A worker voluntarily quits a job to search for a better one. Wrong is employed E A worker switches from working full-time to part-time. Cyclical unemployment is defined as workers losing their jobs due to business cycle fluctuations in output ie.
The SPU is the rate of unemployment such that there are no upward or downward pressures on price inflation apart from those associated with a constant rate of underlying inflation or arising from supply shocks. Cyclical unemployment is the number of people out of work as a result of a temporary setback in the economy such as a recession or change in a business cycle. Frictional Structural unemployment b.
High unemployment rates owe its origin to cyclical unemployment. Structural unemployment is best described as unemployment arising from A the elimination of jobs as a result of technological change B an increase in the number of workers searching for better-paying jobs C an increase in the number of jobs demanding unskilled labor D the temporary reduction of jobs during a downturn in the business. Unemployment arising from a persistent mismatch between the skills and characteristics of workers and the.
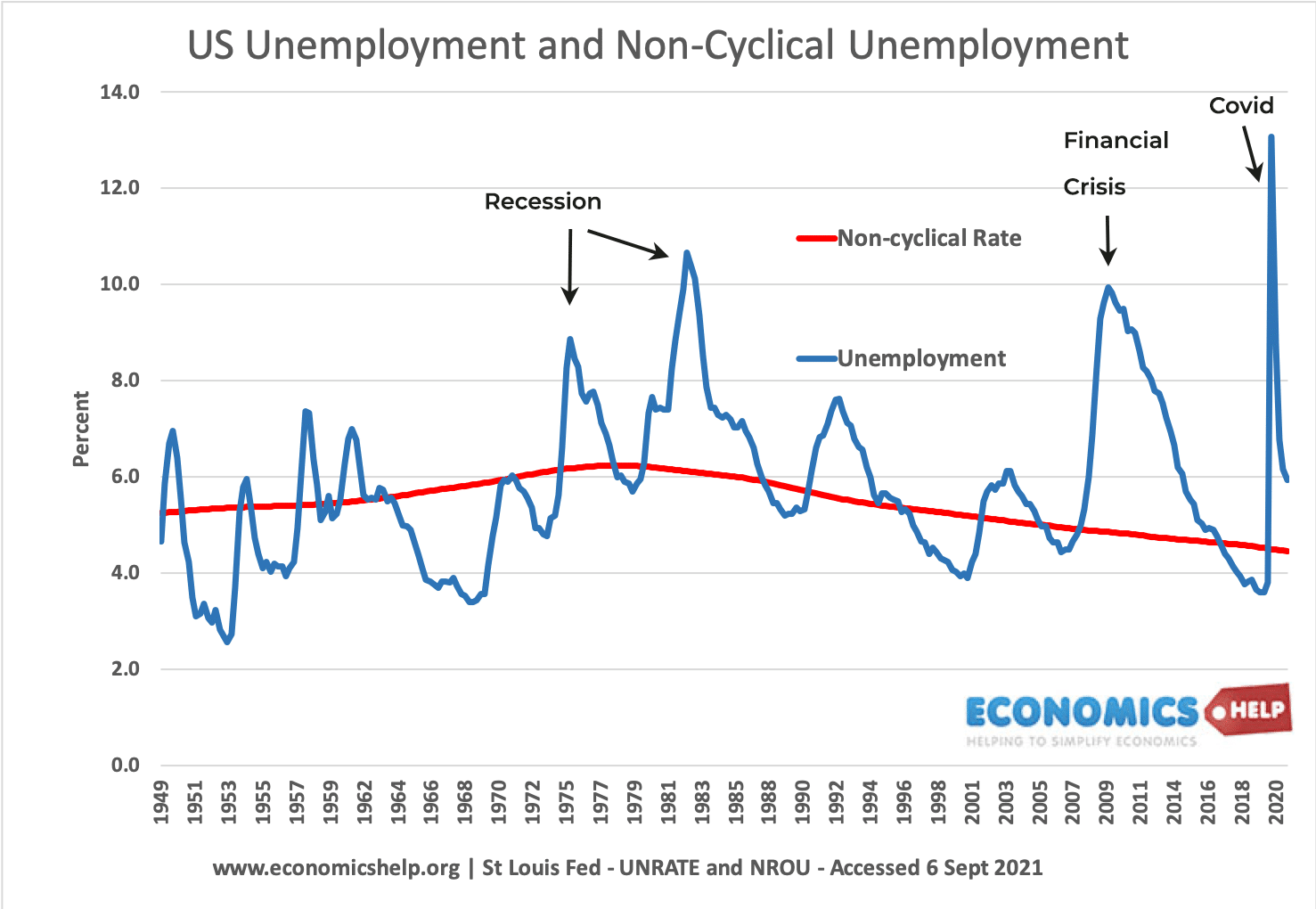
Once recession ceases to exist and economic growth steps forward cyclical unemployment declines. Informally the SPU is the rate of unemployment at which there is no cyclical pressure on inflation. Unemployment refers to people.
C an increase in the number of recent college graduates looking for their first job. Ans b Unemployment arising from economic fluctuations is called. Peaks in unemployment correspond with swings in the economic cycle.
Structural unemployment is best described as unemployment arising from Athe elimination of jobs as a result of technological change Ban increase in the number of workers searching for better-paying jobs Can increase in the number of jobs demanding unskilled labor Dthe temporary reduction of jobs during a downturn in the business cycle. Economics questions and answers. Frictional Cyclical unemployment.
Once again about 5-6 The NRU is often included inside a Free Response Question essay. Structural unemployment is best described as unemployment arising from Athe elimination of jobs as a result of technological change Ban increase in the number of workers searching for better-paying jobs Can increase in the number of jobs demanding unskilled labor Dthe temporary reduction of jobs during a downturn in the business cycle. Cyclical unemployment relates to changes in unemployment due to economic recessions and expansions over the business cycle.
Notice that cyclical unemployment is not part of NRU as the NRU occurs when the economy is at full employment. Underpinning this definition are two. Cyclical unemployment refers to seasonal unemployment caused by economic fluctuations.
Unemployment is given by and the natural rate of unemployment is Select one. B the temporary reduction of jobs during a downturn in the business cycle. When demand for goods and services drops businesses reduce production thereby requiring fewer workers.
Cyclical unemployment results from. Definition Cyclical Unemployment is unemployment due to a period of negative economic growth or economic slowdown. A Who are not willing to work b Who are willing but do not get work c Who leave their jobs in search of better ones d Who have been dismissed because of incorrect practices.
C A worker is laid off because of a downturn in economic activity. Frictional Structural - Cyclical unemployment. A frictional unemployment b disguised unemployment c Cyclical unemployment.
It is the result of downtown in trade fluctuation during recession.

Cyclical Components Of Gdp And The Unemployment Rate In Ireland The Download Scientific Diagram
Comments
Post a Comment